Cradle-to-gate carbon footprint of BioDur biocomposites based products
The key objective of this report is to share potential environmental impacts of Spectalite BioDur biocomposites by using life cycle impact assessment method. This report presents cradle-to-gate climate change impact (global warming potential – carbon footprint) of houseware products made with BioDur.
Carbon footprint of a product presents the life greenhouse gas emissions as part of the process of creating, storing, transporting, using, recycling, or disposing of a product. This report includes cradle-to-gate carbon footprint of houseware products made in USA using BioDur manufactured in India.
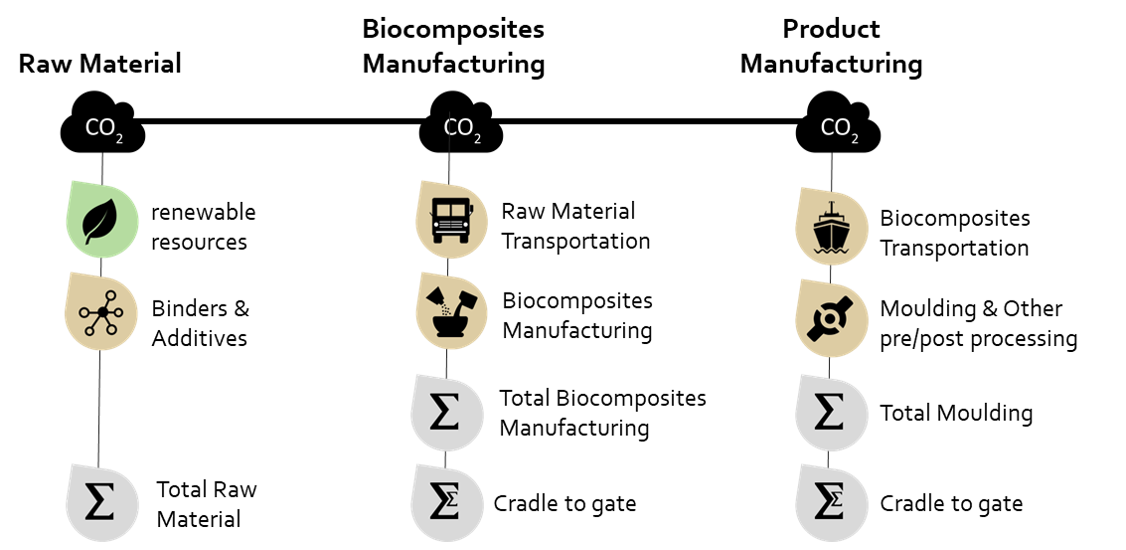
Carbon footprint assessment framework
The cradle-to-grave LCIA assessment is done with following inputs –
- The inventory that has been curated based on reliable datasets and publications.
- The electricity needed to manufacture.
- The renewable content & source.
- The binders & additives used.
- Mode of transport & distance.
- Where possible, we have used actual data.
For this report we have considered injection moulding grade of BioDur biocomposites made with virgin Polypropylene (PP) as the binder. They are sustainable replacements to commonly used PP, PE, ABS, plastics. We have provided relative comparison between these materials and BioDur to understand the ecological benefits.
The actual carbon footprint of the product may vary from this report depending on the final formulation of BioDur, raw materials used and their source.

Relative comparison of carbon footprint
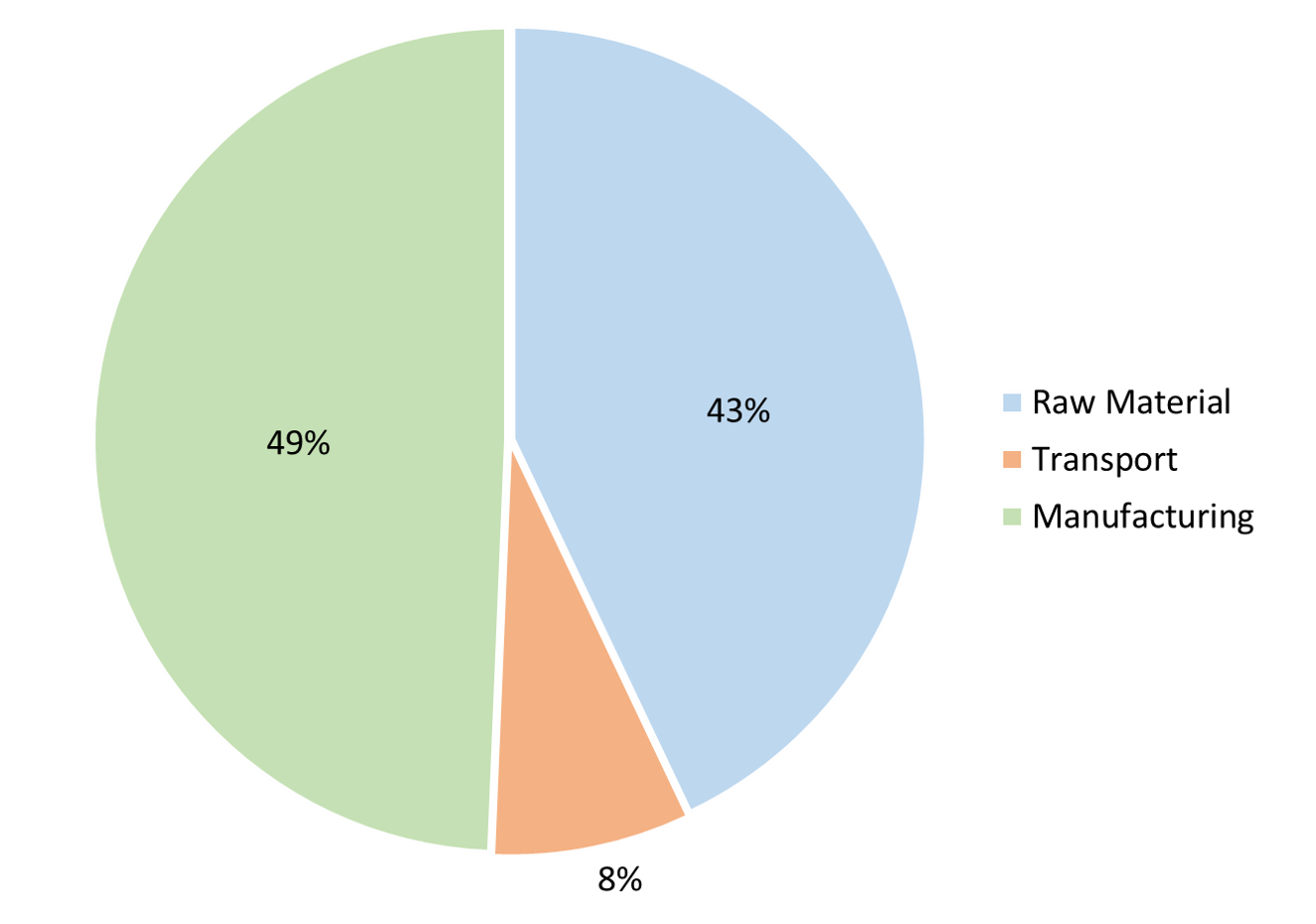
Carbon emissions of BioDur with 40% bamboo fibers
For our conditions & assumptions made, the cradle-to-grave carbon footprint of products made with different proportion of renewable content in BioDur is provided. The renewable content considered here is bamboo waste sourced from a bamboo processing factory in India & bamboo sourced from sustainably managed bamboo farm in India.
Our blockchain technology enables us to share real-time carbon footprint of each batch of our biocomposites manufactured. The technology enables to record and determine the carbon footprint at different stages of the biocomposites product manufacturing process.
Remarks
- The BioDur biocomposites offer best carbon footprint compared to most plastics & composite materials used in thermoplastic process.
- The carbon footprint of BioDur made with bamboo sourced from sustainably managed farm is better than the bamboo waste from the factory. This is due to the additional carbon sequestered in the roots and the soil that can be accounted for in our assessment.
- The main raw materials of BioDur biocomposites are natural fibres and polypropylene binder. By using natural fibre as raw material BioDur biocomposites replace the use of fossil based plastics with renewable raw material sourced sustainably.
- The natural fibers used in BioDur do not result in deforestation and does not compete with food production with verifiable chain of custody using our blockchain technology.
- The proportion of the natural fibre, binder and other additives varies depending on the product application.
- This report is provided for reference only and is valid for specific conditions and assumptions made.






